The Science of Sleep: Foods and Nutrients that help us Rest
Too tired, but not sleeping well enough? Well, sleep isn’t just about feeling tired—it’s a finely tuned biochemical process. Hormones, neurotransmitters, and key nutrients work together to regulate it, and the right foods fuel better sleep, deeper rest, and optimal recovery. Here’s a cheat sheet to help you master it.
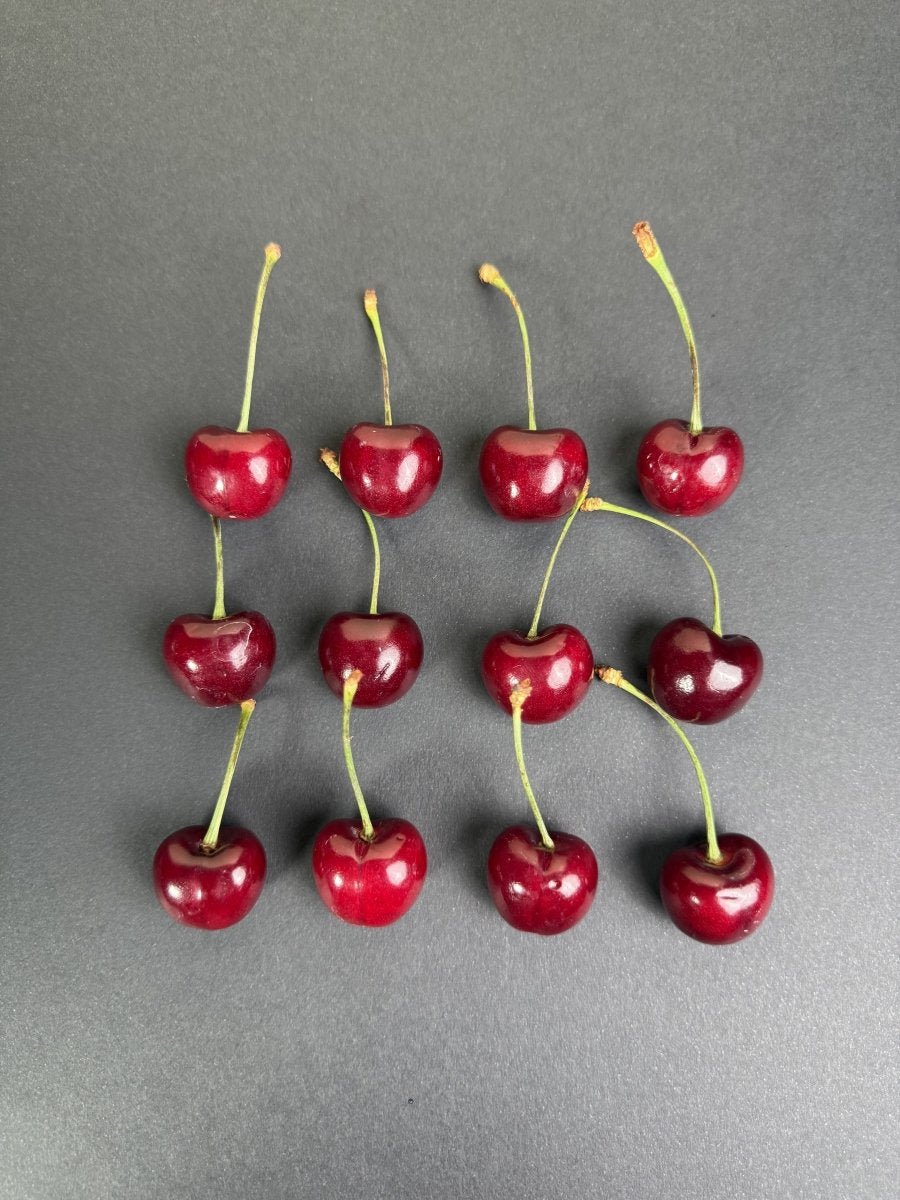
1. Melatonin – The Sleep Hormone
Melatonin signals to your body that it’s time to sleep. Some foods naturally contain melatonin, while others help your body produce more of it.
-
Tart cherries – One of the richest natural sources of melatonin, clinically proven to improve sleep duration.
-
Walnuts – Contain melatonin and omega-3s, which aid its production.
-
Oats – A surprising source of melatonin, making them an excellent bedtime snack.
2. Tryptophan – The Precursor to Serotonin & Melatonin
Tryptophan is an essential amino acid that converts into serotonin (stabilising mood) and melatonin (promoting sleep).
-
Turkey – The classic source (hence the post-dinner-snooze holiday tradition).
-
Milk – Tryptophan + calcium (which helps convert tryptophan into melatonin).
-
Bananas – Provide both tryptophan and magnesium for relaxation.
-
Oats – Offer tryptophan and slow-digesting carbs that help transport it to the brain.
3. Magnesium – The Muscle Relaxer
Magnesium calms the nervous system, regulates melatonin, and reduces cortisol (the stress hormone), all essential for deep sleep.
-
Almonds – High in magnesium and also contain melatonin.
-
Bananas – Magnesium + potassium to relax muscles.
-
Pumpkin seeds – One of the richest sources of magnesium.
-
Dark chocolate – Contains magnesium and serotonin-boosting properties.
4. Omega-3 Fatty Acids – The Brain’s Sleep Aid
Omega-3s support serotonin production and help regulate melatonin. Low levels of it are linked to sleep disturbances.
-
Oil rich fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines) – Omega-3s + vitamin D, which supports serotonin.
-
Walnuts – A plant-based omega-3 source.
-
Flaxseeds & chia seeds – Great for those on a plant-based diet.
5. Vitamin D – The Circadian Rhythm Regulator
Vitamin D plays a role in sleep regulation by supporting serotonin production. Its deficiency is linked to insomnia.
-
Oil rich fish – Again, one of the best natural sources.
-
Egg yolks – contain vitamin D + tryptophan.
-
Mushrooms – The only plant-based source of vitamin D when exposed to sunlight.
The Final Piece: A Ritual for Restful Nights
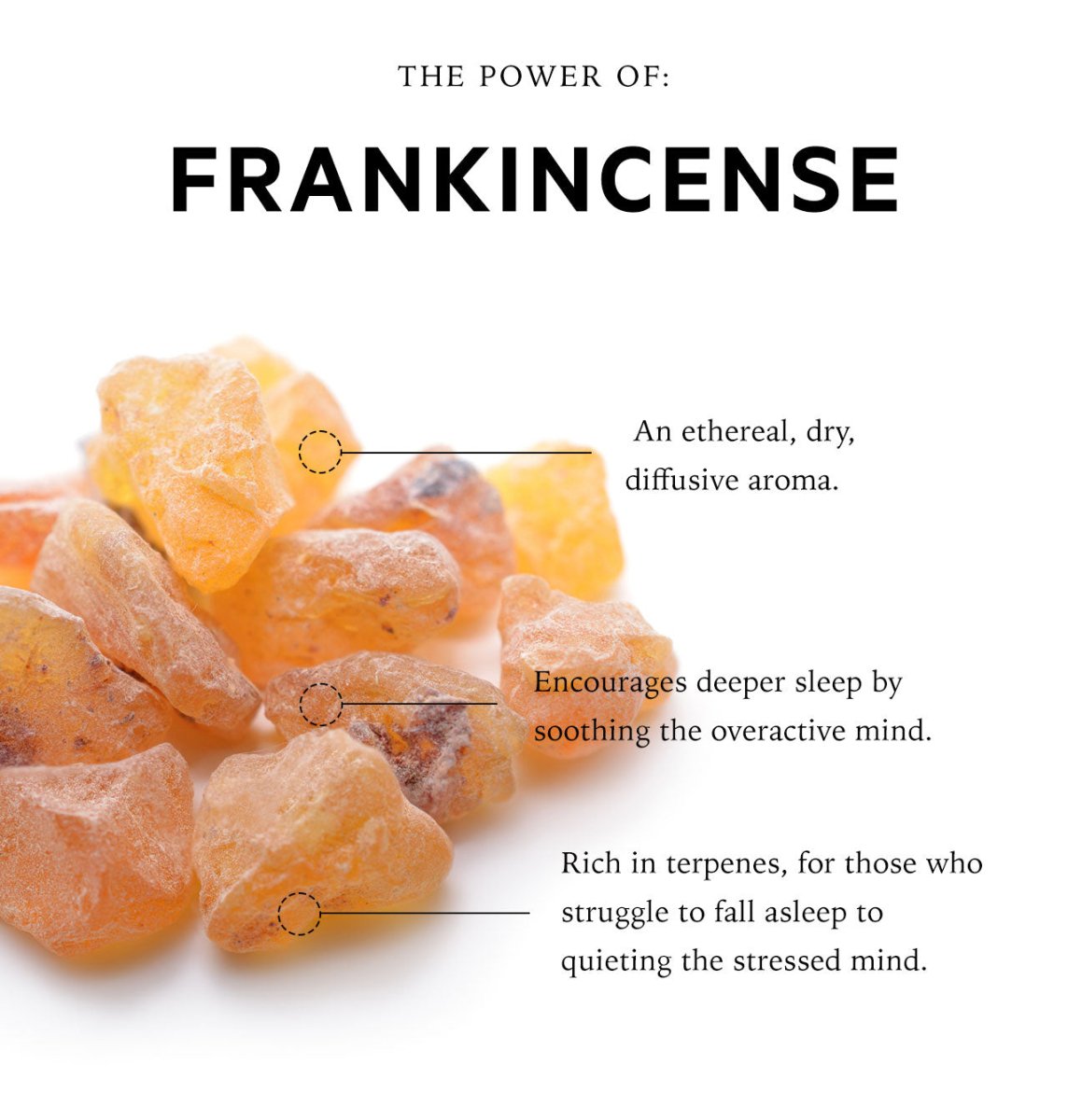
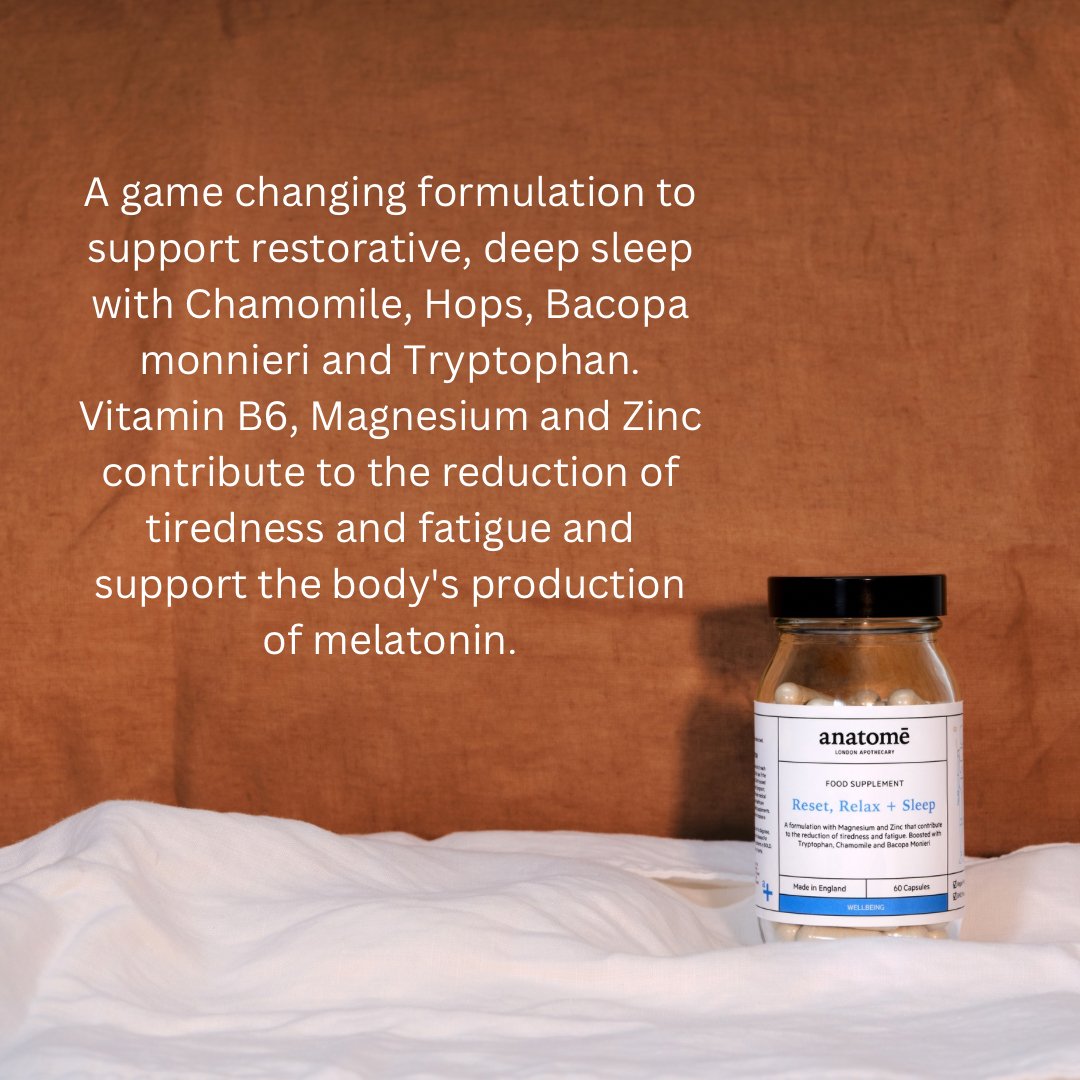
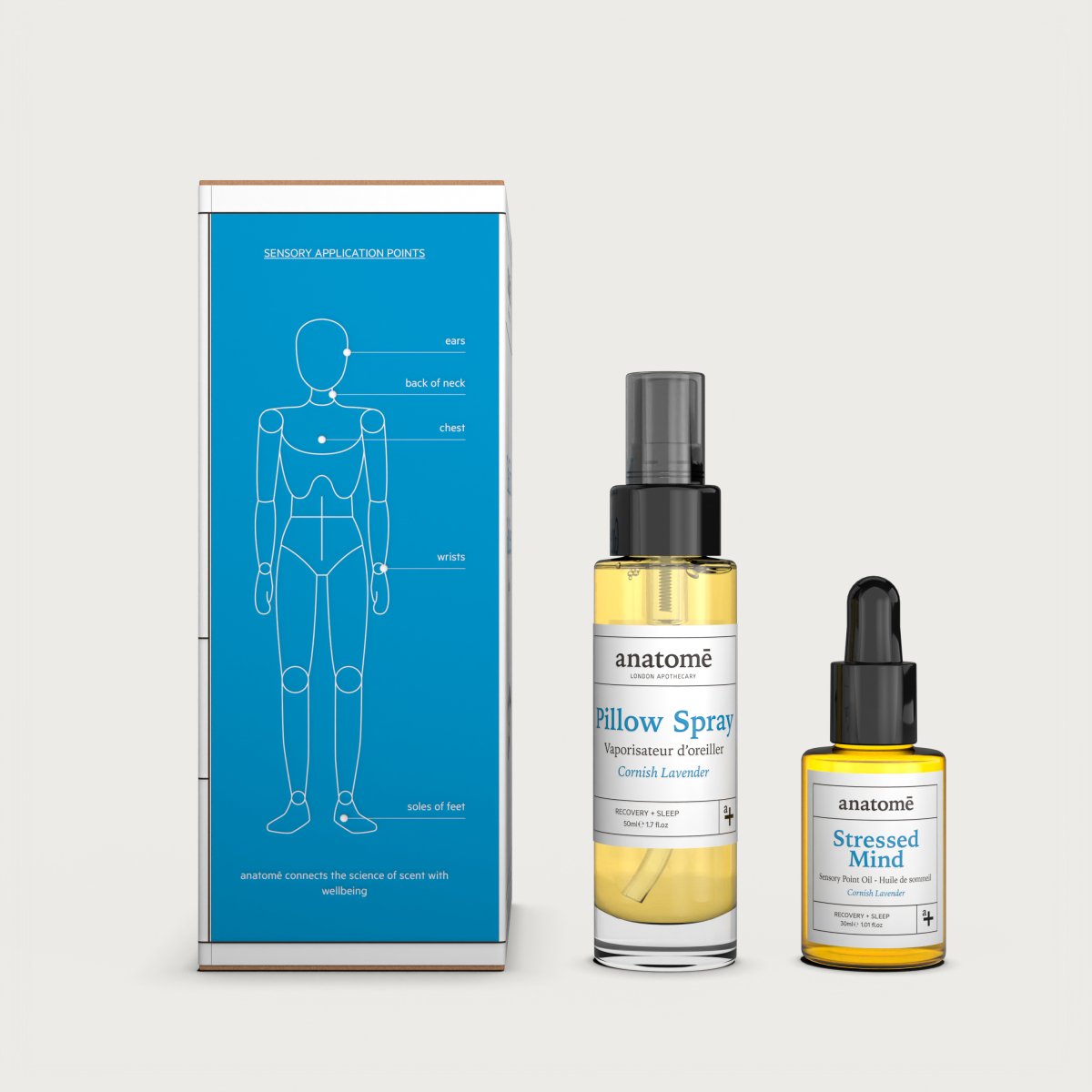
Food can prepare your body for sleep, but pairing it with a proper bedtime practice ensures you unwind properly. anatomē’s Sleep Formulations—including our magnesium-based supplement for deep relaxation and sensory-point oils formulated from calming botanicals—are the ultimate tools for optimising your sleep cycle.